
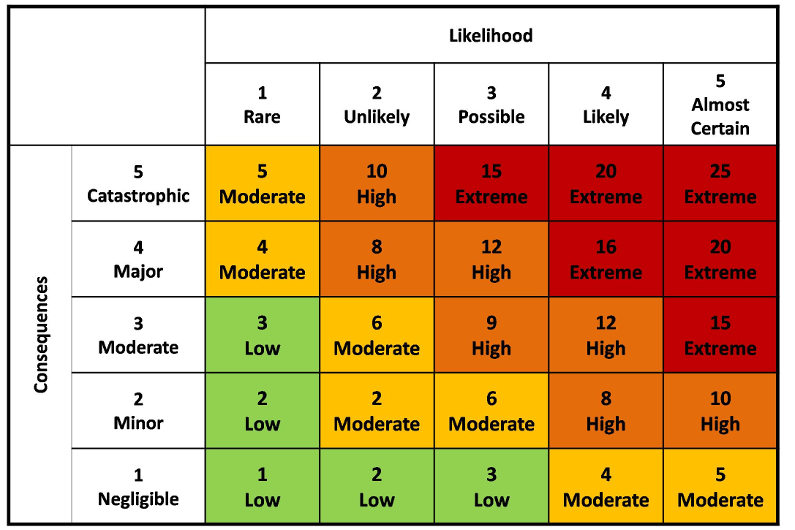
15 This critical literature review highlights the key variables, advantages, disadvantages, strengths and weaknesses of the whole risk analysis phase for the healthcare organizations, engendering a number of recommendations when risk analysis is conducted using a risk matrix.Ī risk matrix method, also called “decision matrix risk assessment (DMRA) technique”, is a systematic approach used in risk assessment process to determine and to rank the risk level, to compare different risks and to define which threats need to be controlled first and to help minimize the probability of potential risks. 12–14 In this context, hospital staff are often called upon to decide whether given risks are high or low, nevertheless participants need clear definitions of what is considered “high” versus “low”. The comparative simplicity and apparent ease of use in this approach likely contributed to widespread adoption, including a generic international standard for risk assessment techniques in support of risk management. 11 One of these methodologies use a qualitative or semi-quantitative risk assessment matrix to identify, assess and rank the risks associated with threats and to determine which threats need to be controlled first. There are different methods of analysis that take into account two common parameters, presence of the hazard and its severity, and they differ in how these two factors are evaluated and combined to estimate the risk. Risk assessment and risk ranking tools have been developed in complex and high-reliability and highly-resilient industries, such as nuclear power generation, manufacturing and aviation have recently been adopted in the healthcare sector, to specifically address patient safety. Healthcare organizations are high-risk and highly complex with multiple dimensions of mutual interdependence (professional, technological, organizational/managerial) and risk management is very important, because even a low-risk event could have serious consequences affecting patients, personnel, costs and the hospital’s reputation. 9, 10 Risk management has become one of the main objectives of individuals, organizations, and governments in pursuing their goals since there is the possibility that things do not go as planned. 7 Thus, risk assessment allows decision-makers to determine, based on the identified and analyzed risks, which risks will be treated and with what priority, becoming a key part of the decision-making process because it can help to identify possible options for risk management, according to the level of risk identified. 2 Risk analysis is finalized to understand the nature, sources and causes of the risks identified and to estimate the level of risk and risk evaluation is used to compare risk analysis results with risk criteria in order to determine whether or not a specified level of risk is acceptable or tolerable and identifying where additional action is required.
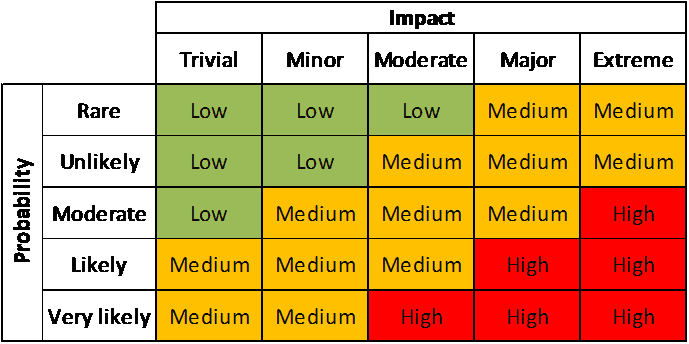
5–8 Risk identification is used to find, recognize and describe the hazard that could affect the achievement of objectives.
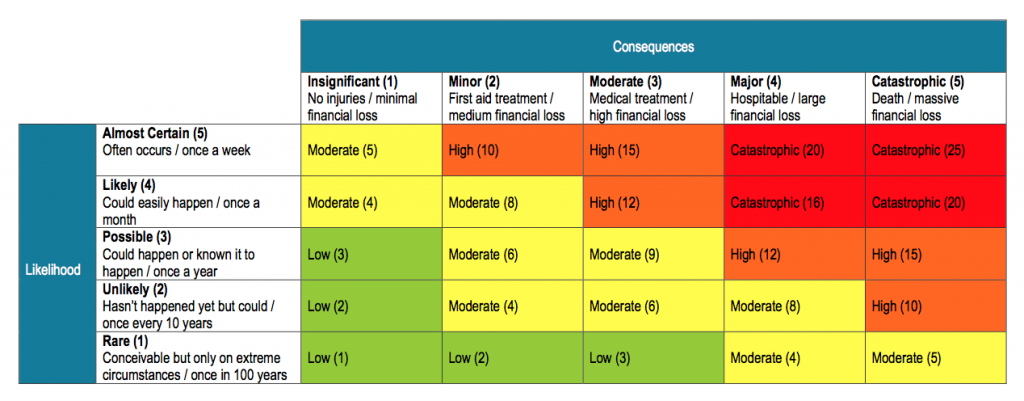
4 In this scheme risk assessment is the term that covers three successive stages: risk identification, risk analysis and risk evaluation.
PROBABILITY CONSEQUENCE MATRIX ISO
3 A general risk management scheme, within the international risk management standards ISO 31000, consist of a few key stages, namely: (i) organizational context definition (ii) risk identification, (iii) risk analysis, (iv) risk evaluation, (v) risk treatment, (vi) monitoring and review, and (vii) communication and consultation, that covers the whole process ( Figure 1). 2 Risk management is defined in the literature as “all the activities connected with hazard identification, assessment, selection of appropriate responses and risk monitoring”. 1 A common definition of risk is “the chance of something happening that will have an impact on the achievement of the stated organizational objectives”. Risk is an essential part of everyday life and risks are unavoidable in any complex program.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
